Tag Chemistry
Madison-made electrolyte going big at global battery manufacturer
Silatronix, a UW–Madison spinoff, says its formulation will lead to safer lithium-ion batteries used in phones, laptops and tablets.
Academic Staff Excellence Awards honor nine campus professionals
Nine members of the University of Wisconsin–Madison's academic staff have been selected as recipients of the 2016 Academic Staff Excellence Awards.
Making molecules comfy: Ultimate challenge for UW’s ‘Glass Guy’
"If you ask an ordinary person, ‘What is glass?’ they will point to a window, but glass is a much broader category of materials,” says Mark Ediger.
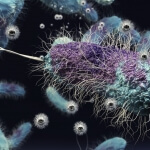
Scientists: Harnessing microbes could help solve hunger, health, chemical and energy problems
Tim Donohue, a UW–Madison bacteriology professor and director of the Great Lakes Bioenergy Research Center, joined 17 other scientists from around the world and representing a wide range of disciplines today (Oct. 28, 2015) to lay out a case for an organized approach to harnessing the power of microbes to tackle many of the world’s most pressing problems.
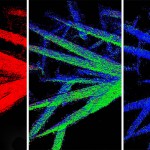
Mother-of-pearl’s genesis identified in mineral’s transformation
How nature makes its biominerals - things like teeth, bone and seashells - is a playbook scientists have long been trying to read.
Tickets available Oct. 1 for Shakhashiri’s science show
There’s only one place that you can find Bucky Badger, Mike Leckrone, and Santa Claus himself doing science experiments – in Professor Bassam Shakhashiri’s lab. Shakhashiri, a professor of chemistry at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, will host his 46th annual holiday science presentation – “Once Upon a Christmas Cheery, In the Lab of Shakhashiri” – on Dec. 5 and 6.
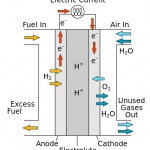
Discovery of a highly efficient catalyst eases way to hydrogen economy
Hydrogen could be the ideal fuel: Whether used to make electricity in a fuel cell or burned to make heat, the only byproduct is water; there is no climate-altering carbon dioxide.
Three UW–Madison professors garner American Chemical Society honors
The American Chemical Society (ACS) has honored three UW–Madison professors with prestigious awards for excellence in research.
Boundless Together: The research behind the commercial
A new commercial for UW–Madison will premier during the season-opening Badger football game on Aug. 5. Learn more about the cutting-edge research highlighted in the spot.
Solar textile collaboration weaves chemistry and design
A new faculty member at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, Marianne Fairbanks is bringing decades of experience with dyes, fibers and design to the development of a technology she's been dreaming of for years: the solar textile.
Cages offer new direction in sustainable catalyst design
University of Wisconsin–Madison engineers have developed a new approach to structuring the catalysts used in essential reactions in the chemical and energy fields. The advance offers a pathway for industries to wean themselves off of platinum, one of the scarcest metals in the earth's crust.
Molecular fuel cell catalysts hold promise for efficient energy storage
In the quest for better, less expensive ways to store and use energy, platinum and other precious metals play an important role. They serve as catalysts to propel the most efficient fuel cells, but they are costly and rare.
Better battery imaging paves way for renewable energy future
In a move that could improve the energy storage of everything from portable electronics to electric microgrids, University of Wisconsin–Madison and Brookhaven National Laboratory researchers have developed a novel X-ray imaging technique to visualize and study the electrochemical reactions in lithium-ion rechargeable batteries containing a new type of material, iron fluoride.
Solution-grown nanowires make the best lasers
Take a material that is a focus of interest in the quest for advanced solar cells. Discover a "freshman chemistry level" technique for growing that material into high-efficiency, ultra-small lasers. The result, disclosed today [Monday, April 13] in Nature Materials, is a shortcut to lasers that are extremely efficient and able to create many colors of light.
Researchers develop new approach that combines biomass conversion, solar energy conversion
In a study published March 9 in Nature Chemistry, University of Wisconsin–Madison chemistry Professor Kyoung-Shin Choi presents a new approach to combine solar energy conversion and biomass conversion, two important research areas for renewable energy.
No joke: Chemistry thesis transmuted into comic book
As thesis writing approached, University of Wisconsin–Madison graduate student Veronica Berns faced a conundrum. She knew how hard it was to describe her work to friends and family — indeed, anybody outside the tight clan of structural chemists. And that was particularly true since she concentrated on a category of should-be-impossible structures called “quasicrystals.” However, Berns liked drawing and using “normal, English-language words,” and so about a year before graduation, she opted to accompany her traditional Ph.D. thesis with a comic book version.