Tag Research
Governor gets firsthand look at future of nuclear energy at UW–Madison
The visit follows a partnership announcement between the Public Service Commission and UW's Department of Nuclear Engineering and Engineering Physics to study nuclear energy opportunities in the state.
DNA analysis provides insight into Mongol Empire’s genetics and integration with local cultures
Are one in 200 men really related to Genghis Khan? Maybe not, according to a new study from researchers at UW–Madison.
IceCube Neutrino Observatory gets a major upgrade beneath the ice
The project ensures that UW–Madison’s efforts at IceCube remain at the forefront of neutrino astronomy for years to come.
Indigenous-led research examines the health of restored manoomin in northern Wisconsin
Wild rice beds are returning to the St. Louis River Estuary thanks to restoration efforts. Ojibwe partners and UW researchers are now looking to determine whether contaminants affect the health of restored manoomin — and those who eat it.
The changing chemistry of invasive death cap mushrooms
UW–Madison researchers just released a revealing study on the mushrooms behind an uptick in poisoning deaths in California.
UW Sea Grant tracks PFAS and other contaminants in bald eagles
Supported by federal funding, the Great Lakes Eagle Health Project investigates how pollutants are affecting the animal’s health — and the environment at large.
Ancient rocks reveal evidence of the first continents and crust recycling processes on Earth
New analyses of the planet’s oldest minerals suggest a diversity of tectonic settings not previously expected more than 4 billion years ago.
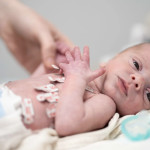
From the lab to the NICU: UW researchers pioneer contactless health monitoring
The system could pave the way for safer, more comfortable patient care in settings ranging from neonatal units to in-home recovery.
Undergraduate research inspires community, confidence and growth
Working in a research lab is helping UW–Madison student Lauren Jacobs get more than hands-on career experience.
Resurrected ancient enzyme offers new window into early Earth and the search for life beyond it
UW researchers are helping us understand the origins of life on Earth and possibly recognize signs of life elsewhere.
How to win a Nobel Prize
Meet the UW–Madison faculty and alumni whose discoveries changed the world.
Microbes mutated in space hint at biomedical benefits to humans on Earth
Researchers are interested in studying effects on the gut microbiome and antibiotic-resistant infections.
The gift of gratitude
UW research scientist and meditation teacher Cortland Dahl explains what's so great about gratitude, no matter the time of year.
UW–Madison top 5 in national research ranking for first time since 2014, surpasses $1.93B in research expenditures
The annual rankings, which cover fiscal year 2024, "highlight the importance of the decades-long partnership between universities and the federal government," says UW–Madison Chancellor Jennifer Mnookin.
Still/Moving
UW–Madison’s capsule of 2025 in striking images.
UW’s Puerto Rican Studies Hub explores the archipelago’s culture and history from a new point of view
The first-of-its-kind center in the Midwest aims to put ‘UW–Madison at the forefront’ of an academic field with growing reach.
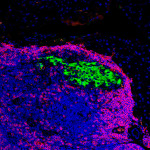
Viruses found in carbon-storing wetlands play an active role in shaping ecosystem health
The viruses could also help determine if a wetland has been damaged or if restoration efforts are working.