Tag Research
Viruses found in carbon-storing wetlands play an active role in shaping ecosystem health
The viruses could also help determine if a wetland has been damaged or if restoration efforts are working.
Detecting and preventing digital abuse
UW–Madison researchers are protecting survivors from cyber stalkers by identifying vulnerabilities in popular phone apps.
This UW–Madison spinoff is making environmentally-friendly cement. The secret ingredient is pollution.
UW–Madison spinoff Alithic is leveraging a unique formula of typically harmful pollutants to produce a key ingredient of concrete.
UW fostering closer research ties with federal defense, cybersecurity agencies
UW–Madison leaders seek to expand partnership with federal agencies to boost dual-use research funding.
With milk testing and new tools, UW scientists are helping prevent bird flu outbreaks in Wisconsin and beyond
The Wisconsin Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory processes samples from every dairy farm in the state to help prevent an H5N1 outbreak among cattle.
Two UW–Madison professors named MacArthur Fellows
Atmospheric scientist Ángel F. Adames Corraliza and nuclear security specialist Sébastien Philippe, professors at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, have been awarded 2025 MacArthur Fellowships.
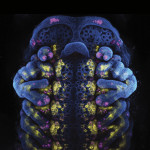
2025 winners of the Cool Science Image Contest
This year’s winners used a variety of tools — from phone cameras to CT scanners — to capture fascinating, surprising and simply beautiful aspects of the natural world.
Scrolling for answers
Hundreds of Wisconsin teens are helping UW researchers study the effects of social media. The findings could be transformative.
Growing the future
UW–Madison’s research stations help Wisconsin farmers stay on agriculture’s leading edge.
UW rises to 36th overall, 12th among publics in U.S. News rankings
UW–Madison’s undergraduate nursing program ranked eighth overall and fifth among publics, and the university’s undergraduate programs also received top 20 rankings in engineering, computer sciences, business, economics and psychology.
A global hub for Hollywood history
UW–Madison’s Wisconsin Center for Film and Theater Research preserves priceless materials from the entertainment industry.
A UW–Madison professor is looking for ways to boost trust in science and public health. Cuts to federal funding are making that work even harder.
UW–Madison professor Michael Xenos and his colleagues are working to ensure vital information is clearly and effectively communicated to people who might not have the most confidence in public health information.