Tag Disease
A Trojan horse? Immune cells ferry deadly fungus from mouse lung into the blood
New research shows how inhaled fungal spores exit the lung and trigger a fatal infection in mice. It appears that lung macrophages abandon their posts as bodyguards and begin smuggling spores into the bloodstream.
PATH Award offers promise for advancing biomedical science at UW–Madison
Assistant Professor John-Demian Sauer has been awarded a 2018 Burroughs Wellcome Award that supports biomedical scientists who are early in their careers and advancing fields in the basic biomedical sciences that are undervalued or underfunded. John-Demian Sauer
Zika virus infection may multiply risk of miscarriage, stillbirth
Researchers at six National Primate Research Centers (NPRCs) combined results from individual studies to find that 26 percent of pregnancies in 50 monkeys infected with Zika virus during the first trimester of pregnancy ended in miscarriage or stillbirth.
In the heart of devastating outbreak, research team unlocks secrets of Ebola
In a study of blood samples from Ebola patients in Sierra Leone, the team led by UW–Madison's Yoshihiro Kawaoka has identified signatures of the disease that may aid in future treatment efforts.
UW-Madison students in Houston to aid post-Harvey mosquito control
To assist efforts to control the millions of mosquitoes that hatched during recent flooding in the Houston area, two University of Wisconsin–Madison students have flown to Texas to help trap and identify them.
An ounce of prevention: Research advances on ‘scourge’ of transplant wards
The fungus Cryptococcus causes meningitis, a brain disease that kills about 1 million people each year - mainly those with impaired immune systems due to AIDS, cancer treatment or an organ transplant. It's difficult to treat because fungi are genetically quite similar to humans, so compounds that affect fungi tend to have toxic side effects for patients.
Genes found in nature yield 1918-like virus with pandemic potential
An international team of researchers has shown that circulating avian influenza viruses contain all the genetic ingredients necessary to underpin the emergence of a virus similar to the deadly 1918 influenza virus.
Making a better flip-flop to overcome illiteracy and disease
In many parts of the world, a good share of the population wears flip-flops. In America, the candy-colored sandals are a ubiquitous herald of summer. In rural Uganda, kids wear them, adult men and moms wear them whether they're bopping around the compound, working in the fields or getting water.
UW scientist sniffs out possible new tick species
In June 2012, Tony Goldberg returned from one of his frequent trips to Kibale National Park, an almost 500-square-mile forest in western Uganda where he studies how infectious diseases spread and evolve in the wild. But he didn’t return alone.
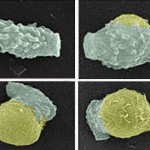
‘Ninja parasites’ elude immune response through molecular mimicry
In feudal-age Japan, cunning, unorthodox mercenaries known as ninjas were notorious for using disguise, deception, and stealth to infiltrate enemy fortifications. In the world of modern parasites, certain organisms - dubbed "ninja parasites" by Professor Timothy Yoshino - use similar tactics, in a biological and chemical sense, to trick their way past the immune systems of their hosts.
UW’s veterinary medical school adopts wildlife health project
Outbreaks of disease in wildlife may seem remote and, for most humans, inconsequential. But disease events that arise in wild animal populations can be far-reaching and can even pose a threat to humans and domestic animals far removed from the source of animal affliction.