X(ray) marks the spot in elemental analysis of 15th century printing press methods

Minhal Gardezi (left) and Uwe Bergmann prepare a leaf of the Gutenberg Bible for scanning. Photo courtesy of Minhal Gardezi. Image provided by Minhal Gardezi
In 15th century Germany, Johannes Gutenberg developed a printing press, a machine that allowed for mass production of texts. It is considered by many to be one of the most significant technological advancements of the last millennium.
Though Gutenberg often receives credit as the inventor of the printing press, sometime earlier, roughly 5,000 miles away, Koreans had already developed a movable-type printing press.
There is no question that East Asians were first. There is also no question that Gutenberg’s invention in Europe had a far greater impact.
“What is not known is whether Gutenberg knew about the Korean printing or not. And if we could shed light on that question, that would be earth shattering,” says Uwe Bergmann, a professor of physics at the University of Wisconsin–Madison who, with UW–Madison physics graduate student Minhal Gardezi, is part of a large, interdisciplinary team that is analyzing historical texts.
He adds: “But even if we don’t, we can learn a lot about early printing methods, and that will already be a big insight.”
These texts include pages from a Gutenberg bible and Confucian texts, and they’re helping investigate these questions. The team includes 15th century Korean texts experts, Gutenberg experts, paper experts, ink experts and many more.
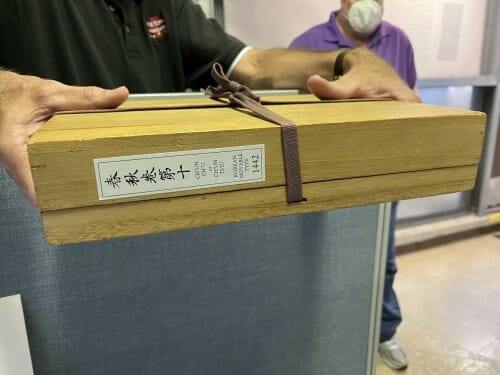
One of the leaves scanned was printed by a Korean movable type printing press in 1442. One of the team members from UNESCO, Angelica Noh, traveled with the preserved documents from Korea to SLAC. Image provided by Minhal Gardezi
How did two physicists end up participating in a seemingly very non-physics cultural heritage project? Bergmann had previously worked on other historical text analyses, where he pioneered the application of a technique known as X-ray fluorescence (XRF) imaging.
In XRF imaging, a powerful machine called a synchrotron sends an intense and very small X-ray beam — about the diameter of a human hair — at a page of text at a 45-degree angle. The beam excites electrons in the atoms that make up the text, requiring another electron to fill in the space left by the first (all matter is made up of atoms, which contain even smaller components called electrons).
The second electron loses energy in the process, and that energy is released as a small flash of light. A detector placed strategically nearby picks up that light, or its X-ray fluorescence, and measures both its intensity and the part of the light spectrum to which it belongs.
“Every single element on the periodic table emits an X-ray fluorescence spectrum that is unique to that atom when hit with a high-energy X-ray. Based on its ‘color,’ we know exactly which element is present,” says Gardezi. “It’s a very high-precision instrument that tells you all the elements that are at every location in a sample.”
With this information, researchers can effectively create an elemental map of the document. By rapidly scanning a page across the X-ray beam, they can create a record of the XRF spectrum at each pixel. One page can produce several million XRF spectra.
This summer, Bergmann and Gardezi were part of a team that used XRF scanning at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory in California to produce elemental maps of several large areas from original pages of a first-edition, 42-line Gutenberg Bible (dating back to 1450 to 1455 A.D.) and from Korean texts dating back to the early part of that. century.
They scanned the texts at a rate of around one pixel every 10 milliseconds, then filtered the data by elemental signature, providing high-resolution maps of which elements are present and in what relative quantities.
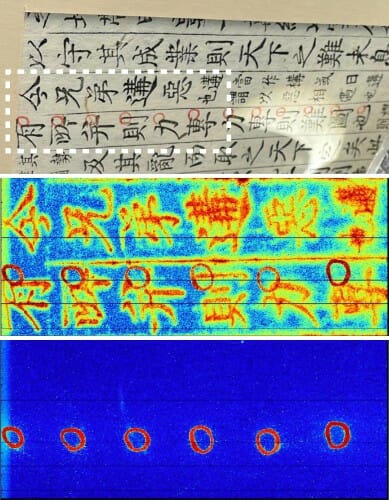
A photograph of a scanned Korean text. The white dotted box indicates the areas shown in the middle and bottom panels. Each element produces a unique X-ray fluorescence. After scanning the text, the researchers applied filters for the known XRF patterns of different elements and created a color-coded heat-map of their abundance, from lowest (blue) to highest (red). An element found in only small quantities is in the red circles in the bottom part of the image. Image provided by Minhal Gardezi
In a way, the work is like digging for treasure from an old map — Gardezi says the researchers do not know exactly what they are looking for, but they are most interested in the unexpected.
For example, she recently presented early results of scans to the team, to demonstrate the approach had worked and that the researchers could separate out different elements. It turns out this isn’t what the team found most interesting.
“Instead, these scholars spent 15-to-20 minutes talking about, ‘Why is (this element) present?’ and coming up with hypotheses,” Gardezi says. “As physicists, we wouldn’t even recognize if something is surprising or not. It’s really this interdisciplinary aspect that tells us what to look for, what the smoking gun is.”
As more questions arise based on the elemental analyses, Bergmann and Gardezi will help guide the team to address those questions quantitatively. They are already planning to recreate some early printings in the lab — with known types, papers and inks — then compare these XRF scans with the originals.
The research may never definitively determine if Gutenberg knew about the Korean presses or if he developed his press independently. But without access to the original presses themselves, these texts hold the only clues to understanding the nature of these transformative machines.
“The more you read about it, the more you learn that there is less certainty about several things related to early printing presses,” Bergmann says. “Maybe this technique will allow us to view these prints as a time capsule and gain invaluable insight into this watershed moment in human history.”
Watch Minhal Gardezi show off XRF at SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory.
The UW–Madison efforts in the project are supported by the Overseas Korean Cultural Heritage Foundation.