Category Science & Technology
Shaw awards go to two UW researchers
One scientist studying how HIV spreads in the body and another examining cellular machinery and its role in disease have earned funding from the Greater Milwaukee Foundation to advance their research.
New tumor-targeting agent images and treats variety of cancers
Scientists at the University of Wisconsin Carbone Cancer Center (UWCCC) report that a new class of tumor-targeting agents can seek out and find dozens of solid tumors, even illuminating brain cancer stem cells that resist current treatments.
Genes found in nature yield 1918-like virus with pandemic potential
An international team of researchers has shown that circulating avian influenza viruses contain all the genetic ingredients necessary to underpin the emergence of a virus similar to the deadly 1918 influenza virus.
Long lost WWII soldier returned to family with help of UW–Madison scientists
No longer missing, Pfc. Lawrence S. Gordon is finally on his way home.
Mobile sustainability game spurs students to take environmental action
Traversing the University of Wisconsin–Madison campus while consulting iPads and smartphones, the students in Cathy Middlecamp’s introductory environmental studies course could have been mistaken for anyone checking social media en route to class. But for these students, class was already in session. Middlecamp, a professor in the Nelson Institute for Environmental Studies, partnered with the UW Mobile Learning Incubator to have students in Environmental Studies 126 playtest a new mobile game under development that explores sustainability features on the UW–Madison campus.
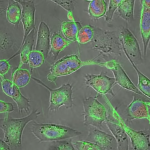
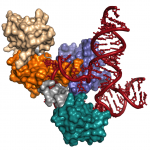
Scientists capture most detailed images yet of tiny cellular machines
A grandfather clock is, on its surface, a simple yet elegant machine. Tall and stately, its job is to steadily tick away the time. But a look inside reveals a much more intricate dance of parts, from precisely-fitted gears to cable-embraced pulleys and bobbing levers.
UW-Madison links with New York museum to collect games and learning data
Leaning over a multitouch table, middle schoolers examine a digital underwater environment, shifting blocks across the screen and building lures to capture computerized fish. While the game introduces engineering principles and logic through an entertaining vehicle, the surface of the table is only half the story.
Beginning of time to unfold at UW–Madison Space Place
Eavesdrop on the beginning of time this Friday evening (May 30, 2014) at the University of Wisconsin–Madison's Space Place, 2300 S. Park St.
Buried fossil soils found to be awash in carbon
Soils that formed on the Earth’s surface thousands of years ago and that are now deeply buried features of vanished landscapes have been found to be rich in carbon, adding a new dimension to our planet’s carbon cycle.
Tinkering fosters business success for Internet of Things Lab
At first, the students considered creating an app or a smart device. But when they got down to it, they decided simplicity really is bliss.
The color of blood: Pigment helps stage symbiosis in squid
The small but charismatic Hawaiian bobtail squid is known for its predator-fooling light organ.
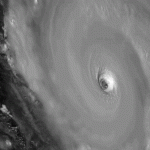
Study shows tropical cyclone intensity shifting poleward
The latitude at which tropical cyclones reach their greatest intensity is gradually shifting from the tropics toward the poles at rates of about 33 to 39 miles per decade, according to a study published today (May 14, 2014) in the journal Nature.
Mackie to receive highest honor in medical physics
Thomas "Rock" Mackie, director of medical engineering at the Morgridge Institute for Research, will receive the highest honor in the field of medical physics for his far-reaching contributions to medical imaging.
Research by UW shapes national climate report
University of Wisconsin–Madison researchers, including many affiliated with the Nelson Institute, contributed to the third U.S. National Climate Assessment released by the White House on May 6.
Citizen scientists provide clarity for lake researchers’ big questions
A massive new study of water clarity trends in Midwestern lakes is sure to make some waves in scientific circles. The study involved nearly a quarter of a million observations in 3,251 lakes spread across eight states, and data dating back seven decades. But it’s where that data came from that’s truly noteworthy. For the report, published online April 30 in the journal PLOS ONE, researchers turned exclusively to citizen scientists.
De-extinction: Will dead species live again?
De-extinction is a recent term that involves bringing back an extinct species using DNA that’s been recovered from preserved material. There are two ways that it can be accomplished: one would be cloning to produce a copy of an extinct individual’s genome. The second way is through genetic engineering to re-create a close approximation of what the extinct species’ genome might have once been. The reality is that it’s no longer science fiction. We’re getting close to being able to revive extinct species from recovered DNA.