Tag Research
UW-Madison undergraduates make unwelcome discovery in Lake Mendota
On Sept. 11, a standard cruise on Lake Mendota's University Bay began for students in University of Wisconsin–Madison's Zoology 315, a course that introduces them to the study of lakes. With the sampling craft Limnos anchored about one-quarter mile offshore on a clear sunny day, four students pulled up a small net and began poking through its contents.
UW-Madison entomologist helps farmers deal with tricky crop pest
Historically, crop rotation has worked to keep the western corn rootworm in check in Wisconsin.
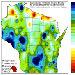
Study reveals dynamic Wisconsin climate, past and future
If the future scenarios being churned out by the world's most sophisticated computer climate models are on the mark, big changes are in store for Wisconsin's weather during the next century.
Research aims to cool runoff to protect coldwater streams
The ocean of stormwater that flows off of the sun-baked urban landscape is packing heat, and trout are starting to feel it.
Potato blight reveals some secrets as genome is decoded
Late blight caused the 19th century famine that sparked a wave of emigration from Ireland to the United States, but the disease has also infected tomatoes and potatoes this year. Potatoes, the world's fourth-largest food crop, were raised on 65,500 acres in Wisconsin in 2007. If a potato field is not treated with pesticide, late blight can destroy the crop in a few days.
Science and media disconnect? Maybe not, says a new study
The prevailing wisdom among many scientists and scientific organizations is that, as a rule, scientists are press shy, and those who aren't are mavericks.
Late blight won’t affect availability or quality of Wisconsin’s potato crop
News about late blight has raised concerns among retailers, processors and other users about the availability and quality of stored potatoes in Wisconsin this winter, reports A.J. Bussan, University of Wisconsin–Madison extension vegetable specialist. But Bussan doesn't think that either quality or quantity will be a problem.
Monkeys get a groove on, but only to monkey music
Music is one of the surest ways to influence human emotions; most people unconsciously recognize and respond to music that is happy, sad, fearful or mellow. But psychologists who have tried to trace the evolutionary roots of these responses usually hit a dead end. Nonhuman primates scarcely respond to human music, and instead prefer silence.
UW-Madison’s ‘good ideas’ get lift from stimulus funds
The university has drawn more than $38 million in funding for more than 120 research projects and programs from the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act. The work is spread across the range of academic disciplines, including public health, computer science, psychology, economics and engineering. Funding comes from agencies such as NSF, the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the Department of Energy and the National Endowment for the Arts.
Snaring bigger bugs gave flytraps evolutionary edge
Carnivorous plants defy our expectations of how plants should behave, with Venus flytraps employing nerve-like reflexes and powerful digestive enzymes to capture and consume fresh meat. The evolutionary history of these botanical oddities is now a bit clearer, thanks to new work.
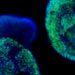
Wisconsin team grows retina cells from skin-derived stem cells
A team of scientists from the University of Wisconsin–Madison School of Medicine and Public Health has successfully grown multiple types of retina cells from two types of stem cells - suggesting a future in which damaged retinas could be repaired by cells grown from the patient's own skin.
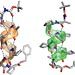
A new ‘bent’ on fusion
Success in cellular fusion - as occurs at the moment of conception and when nerve cells exchange neurotransmitters - requires that a membrane be bent before the merging process can begin, University of Wisconsin–Madison researchers have shown.
New approach to wound healing may be easy on skin, but hard on bacteria
In a presentation today (Aug. 19) to the American Chemical Society meeting, Ankit Agarwal, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, described an experimental approach to wound healing that could take advantage of silver's anti-bacterial properties, while sidestepping the damage silver can cause to cells needed for healing.
Research shows advertisers new ways to hunt for TV bargains
The scene is played out in living rooms across America daily: A favorite television show builds to its riveting conclusion, and a commercial for fast food, automobiles or laundry detergent fills the screen.
Engineered protein-like molecule protects cells against HIV infection
With the help of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and molecular engineering, researchers have designed synthetic protein-like mimics convincing enough to interrupt unwanted biological conversations between cells.
Future angst? Brain scans show uncertainty fuels anxiety
Anyone who has spent a sleepless night anguishing over a possible job loss has experienced the central finding of a new brain scan study: Uncertainty makes a bad event feel even worse.
Scientists make multiple types of white blood cells directly from embryonic and adult stem cells
In an advance that could help transform embryonic stem cells into a multipurpose medical tool, scientists at the University of Wisconsin–Madison have transformed these versatile cells into progenitors of white blood cells and into six types of mature white blood and immune cells.
GLBRC receives $8 million in Recovery Act funding
The Department of Energy (DOE) Great Lakes Bioenergy Research Center (GLBRC) has received $8.099 million in new funding from the U.S. Department of Energy through the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act to provide crucial support for plant cell wall imaging and sustainability research.
Early Alzheimer’s screenings could cut health care costs
As the nation debates how to control costs as part of health care reform, an Alzheimer's disease researcher says early diagnosis and treatment of the disease could save the nation billions of dollars in costs down the road.
Gasoline-diesel cocktail: a potent recipe for cleaner, more efficient engines
Diesel and gasoline fuel sources both bring unique assets and liabilities to powering internal combustion engines.