Category Science & Technology
Workshop to focus on policy innovation for environmental, economic gain
How can the U.S. and the European Union find solutions to environmental problems while also supporting the economy? Eight Europeans with expertise in creating and using new policies to meet 21st century environmental and economic challenges will be in Madison June 19 at Monona Terrace as part of an open-to-the-public "international dialogue on ecological policy" co-sponsored by the University of Wisconsin–Madison.
Virtual chemistry experiments snag big Internet award
A Journal of Chemical Education Web site produced at UW–Madison has received a major "internetional" award.
Computer scientists set on winning the computer virus ‘cold war’
First came the virus. Then came the antivirus software. Ever since, virus programmers have been escalating their technology, trying to stay one step ahead of the computer security engineers and vice versa.
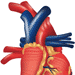
Research may yield improved treatment for diseased lungs
A multi-institutional team of engineers, scientists and clinicians from the University of Wisconsin–Madison will study large-artery biomechanics that could play a role in heart failure in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Student race car design team takes first place
The University of Wisconsin–Madison Formula SAE Racing student vehicle team took first place at the international competition in Detroit.
UW study to clarify safety, effectiveness of hormone therapy during menopause
When is the best time in a woman's reproductive history to start hormone therapy? How does estrogen therapy affect a woman's cognition and mood? What is the most beneficial form of estrogen? These are just a few important questions that researchers at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health hope to answer in a federally funded nationwide study, the first of its kind, on the effects of estrogen therapy with perimenopausal women.
Study explores effectiveness of rain gardens
Although many rain gardeners swear by prairie plants and other native species, vegetation plays a lesser role than other factors in how well rain gardens trap storm water runoff and coax it into the ground, according to a recent UW–Madison study.
Curiosities: Why do we have fingernails?
Fingernails are essentially flattened versions of claws, and they evolved in all primates — including humans — to support broad fingertips, says UW–Madison anthropology…
Research aims to make it easier to serve local produce as classroom snacks
Wisconsin Homegrown Lunch, a partnership between a UW–Madison center and a local nonprofit organization, is working to introduce locally grown products into elementary schools around the area.
Unique engine-centered master’s program graduates first class
A master of engineering program that began out of a lunch conversation between University of Wisconsin–Madison faculty and industry professionals is graduating its first class of 10 students this week.
UW establishes stem cell and regenerative medicine center
In an effort to strengthen and sustain its leadership in the companion fields of stem cell research and regenerative medicine, the University of Wisconsin–Madison will establish a new Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine Center.
Bike ride will raise funds to educate dairy, livestock farmers
On Sunday, June 10, a couple of dozen intrepid bicyclists will pump up their tires and roll out of the driveway of a farm northwest of Antigo to begin the fourth annual Ride to Farm.
Decoding protein structures helps illuminate cause of diabetes
Any photographer can vouch for the difficulty of capturing a clear picture of a moving target. When it comes to molecules, however, sometimes the motion is exactly what scientists want to see.
State seeds stem-cell company based on UW–Madison research
Governor Jim Doyle today (May 14) gave a $1 million boost to a University of Wisconsin–Madison spin-off company during a visit to the campus lab that gave birth to its technology.
Curiosities: If we think the continents were at some point all connected, how did they separate?
Question submitted by Abbie Stroup, seventh grader at Sennett Middle School.
Creator of Dolly the sheep to give public lecture in Madison
Ian Wilmut, the famed Scottish biologist who created Dolly the cloned sheep, is coming to Madison and will give a public lecture on Thursday, May 17, at the Overture Center.
Meditation may fine-tune control over attention
Everyday experience and psychology research both indicate that paying close attention to one thing can keep you from noticing something else.