Tag School of Medicine and Public Health
HealthDay writer named biomedical writer in residence
HealthDay writer Amanda Gardner has already made the transition many other journalists now face — from writing for the print media to the virtual world. Gardner will be the School of Medicine and Public Health’s biomedical writer in residence the week of March 30.
UW-Madison medical student invited to White House for health care reform forum
Last December, when Siavash Sarlati responded to President-elect Barack Obama's national challenge and organized an informal health care reform discussion group in his father's Milwaukee home, he never dreamed it would turn into a trip to the White House.
Chemistry meets biology at screening center
When University of Wisconsin–Madison bacteriologist Nancy Keller and her team managed to genetically trick fungi into making metabolic byproducts that are notoriously difficult for scientists to get at, she wondered if the substances might have any clinically useful properties.
Genetic information personalizes warfarin prescribing
Warfarin, one of the world's most widely used drugs, is also one of the trickiest to prescribe. Half of those who take it are at risk of serious problems when given the standard starting dose.
How do you mend a broken heart? Maybe someday with stem cells made from your skin
A little more than a year after University of Wisconsin–Madison scientists showed they could turn skin cells back into stem cells, they have pulsating proof that these "induced" stem cells can indeed form the specialized cells that make up heart muscle.
Single gene lets bacteria jump from host to host
All life - plants, animals, people - depends on peaceful coexistence with a swarm of microbial life that performs vital services from helping to convert food to energy to protection from disease.
Early childhood stress has lingering effects on health
Stressful experiences in early childhood can have long-lasting impacts on kids' health that persist well beyond the resolution of the situation.
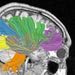
Protein that regulates hormones critical to women’s health found in pituitary
University of Wisconsin–Madison researchers have solved the mystery surrounding a "rogue protein" that plays a role in the release of neurotransmitters and hormones in the brain.
Kemnitz to step down as Primate Center director
Joseph W. Kemnitz, who has led Wisconsin's National Primate Research Center (WNPRC) for more than a decade, announced this week (Jan. 9) that he plans to step down from his position as director of the center and return to the faculty at the end of 2009.
Study: Risky behavior prominent on teen MySpace profiles
More than half of adolescent MySpace users mention risky behaviors such as sex, violence or substance use on their personal Web profiles.
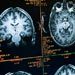
Expectant brains help predict anxiety treatment success
A network of emotion-regulating brain regions implicated in the pathological worry that can grip patients with anxiety disorders may also be useful for predicting the benefits of treatment.
Clinical trial uses bat saliva enzyme for stroke treatment
Vampires aren't usually cast in the role of saviors, but stroke experts are hoping a blood thinner that mimics a chemical in vampire saliva will help save brain cells in stroke patients. The School of Medicine and Public Health is one of several centers worldwide currently enrolling patients in a large new clinical trial of desmoteplase, a drug based on an enzyme in vampire bat saliva.
Cognitive computing: Building a machine that can learn from experience
A UW–Madison researcher says the goal of building a computer as quick and flexible as a small mammalian brain is more daunting than it sounds.
Can milk help prevent transplant rejections?
Could Wisconsin's signature product – milk – hold the key to one of the biggest problems in organ transplantation? Hans Sollinger, the surgeon who heads the transplant program at UW Hospital and Clinics, is betting on it.
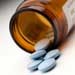
Will the economy prompt greater use of generic drugs?
The expense of the daily dose of medicine is a bitter pill for many Americans. Yet, more than half of those taking prescription drugs are not taking advantage of an economical option: generic drugs.
Initiative positions Wisconsin to become leader in personalized medicine
Wisconsin may soon become an international leader in personalized medicine, a simple concept that has the potential to revolutionize healthcare.